In the fast-paced world of modern society, where convenience often trumps nutrition, many individuals unknowingly suffer from vitamin deficiencies. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being, but due to various factors such as poor dietary choices, restrictive diets, and lifestyle habits, the prevalence of common vitamin deficiencies has surged. In this article, we will explore the most prevalent vitamin deficiencies in the US and worldwide, shedding light on their potential consequences and ways to prevent and address them.
Understanding the Importance of Vitamins
Before delving into specific deficiencies, let’s grasp the significance of vitamins in our bodies. Vitamins are organic compounds that our bodies need in small quantities to perform vital functions.
These include maintaining healthy immune systems, supporting energy production, promoting cell growth, and assisting in countless enzymatic reactions. While vitamins are present in various foods, their absence or inadequacy can lead to deficiency-related health issues.
Common Vitamin Deficiencies in the World
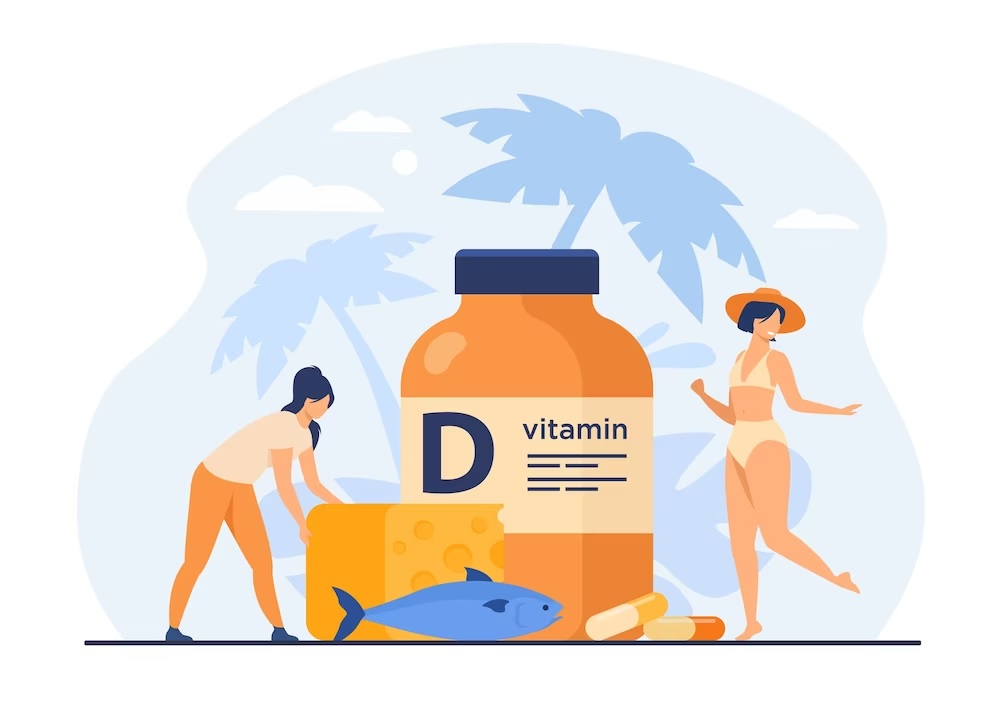
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is essential for calcium absorption, bone health, and immune system function. Despite its name, Vitamin D is more accurately classified as a hormone, and it can be synthesized in the skin when exposed to sunlight. However, modern lifestyles characterized by indoor jobs and limited outdoor activities have contributed to a widespread deficiency of this crucial nutrient.
- Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency can lead to weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Additionally, inadequate vitamin D levels have been linked to compromised immune function, contributing to a higher susceptibility to infections and chronic diseases.
- Prevention and Treatment: To prevent vitamin D deficiency, it’s essential to spend some time outdoors each day, especially in sunlight-rich environments. Dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks. For severe deficiencies, supplements prescribed by healthcare professionals may be necessary.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function, red blood cell production, and DNA synthesis. While it is naturally present in animal-based foods, individuals adhering to vegan or vegetarian diets may face a higher risk of deficiency.
- Consequences of Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Untreated vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to pernicious anemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems like tingling sensations or memory loss. If left unaddressed, severe cases of B12 deficiency can result in irreversible nerve damage.
- Prevention and Treatment: To prevent vitamin B12 deficiency, individuals following plant-based diets should consider fortified foods or B12 supplements. For those with absorption issues, vitamin B12 injections or sublingual supplements may be recommended.
Most Common Vitamin Deficiencies in the United States
Vitamin E Deficiency in the United States
Vitamin E deficiency is a prevalent issue in the United States, with approximately 8 out of 10 individuals not meeting the recommended intake of this fat-soluble antioxidant. Vitamin E is crucial for protecting cells from oxidative damage and supporting the immune system.
- Consequences: The consequences of vitamin E deficiency can manifest as muscle weakness, vision problems, and a weakened immune response. In the long term, insufficient vitamin E intake may increase the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer.
- Prevention and Treatment: Preventing vitamin E deficiency involves incorporating foods rich in this vitamin into the diet. Common sources include nuts (almonds, hazelnuts), seeds (sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds), vegetable oils (sunflower oil, safflower oil), and leafy green vegetables (spinach, Swiss chard).
Addressing vitamin E deficiency can be achieved through dietary changes or supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Vitamin A and Vitamin C Deficiency in the United States
The deficiency of vitamin A and vitamin C affects approximately 50 percent of the American population. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin necessary for vision, immune function, and skin health. Vitamin C is a water-soluble antioxidant crucial for the immune system and collagen synthesis.
- Consequences: Vitamin A deficiency can lead to night blindness, increased susceptibility to infections, and impaired growth and development in children. Vitamin C deficiency can cause scurvy, characterized by fatigue, bleeding gums, joint pain, and delayed wound healing.
- Prevention and Treatment: Preventing deficiencies in these vitamins can be achieved by consuming a diverse diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
Treating vitamin A and vitamin C deficiencies often involves improving dietary intake. For severe cases, supplementation may be recommended by a healthcare professional.
Vitamin D Deficiency in the United States
More than 50 percent of the general population in the United States is vitamin D deficient, regardless of age. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for calcium absorption, bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
- Consequences: Vitamin D deficiency can lead to weakened bones, increased risk of fractures, muscle pain, and a compromised immune system. Inadequate vitamin D levels have been associated with an increased risk of certain chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Prevention and Treatment: Preventing vitamin D deficiency involves a combination of dietary sources and exposure to sunlight. Foods rich in vitamin D include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products (milk, yogurt), and egg yolks. Moderate exposure to sunlight is essential, especially for individuals living in regions with limited sunlight during certain seasons.
Treating vitamin D deficiency may require vitamin D supplementation, especially in cases where dietary intake and sun exposure are insufficient. Healthcare professionals can guide individuals on appropriate dosages based on individual needs and blood test results.
Conclusion
Common vitamin deficiencies pose a significant health concern. With poor dietary choices, restrictive diets, and sedentary lifestyles becoming more prevalent, essential nutrients often take a backseat. Vitamin D deficiency stands out as a widespread issue, affecting more than half of the American population, leading to weakened bones and compromised immunity. Additionally, vitamin E, vitamin A, and vitamin C deficiencies affect a significant portion of the population, contributing to various health problems. Preventing these deficiencies requires adopting a balanced diet, considering dietary supplements if necessary, and embracing outdoor activities to soak in the benefits of sunlight. Understanding the importance of vitamins and addressing deficiencies promptly can foster a healthier and more vibrant society.